Plan Applications
Review Essays
Scholarship Finder
Activity Feedback
Plan Applications
Review Essays
Scholarship Finder
Activity Feedback
Plan Applications
Review Essays
Scholarship Finder
Activity Feedback
Plan Applications
Review Essays
Scholarship Finder
Activity Feedback
TAILORED JUST FOR YOU
Drawing on thousands of data points to find your perfect match.
Discover opportunities that align with your goals, interests, and life stage; no guesswork, just what fits.

PERSONALISED FINANCIAL AID AI
Scholarships that don’t ghost you.
Stay in the loop with scholarships that actually respond, support, and show up.
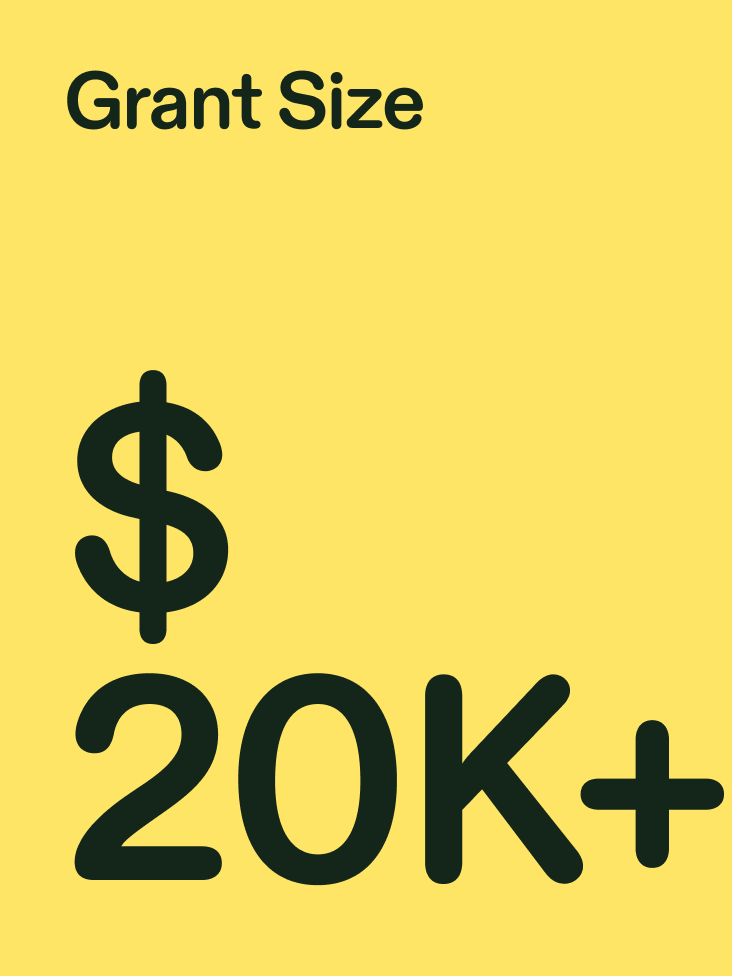
24/7 AI ESSAY SUPPORT
Essays, Demystified.
Get step-by-step support to write essays that sound like you — and stand out.
UNLEASH YOUR FULL POTENTIAL
And dozens of other tools to get you where you need to be
Powered by Kollegio AI
Make your perfect college list in minutes
Create your perfect college list in minutes. Save your list with Kollegio to start planning your next move.


FROM OTHERS AROUND THE WORLD
Don’t just take it from us

Annabel
Portola High School, CA
College applications can be very stressful but Kollegio has made it much easier! I can see which colleges fit my preferences based on my profile and get detailed feedback for all my essays. Best of all, everything is completely free! Would definitely recommend!

Meher
Edison High School, NJ
Kollegio has really helped me with evaluating my essays and getting quick feedback on my essay structure! It's a much needed companion tool to the traditional college admission services, and I'm so glad that it's free because every student can benefit from it.

Claryssa
Community College, CA
Kollegio helped me brainstorm ideas for essays that were tailored to my experiences, while still giving me the freedom and creativity to write my essays entirely on my own. Their support made applying to college smoother and more personal, allowing me to tell my story authentically.

Cyril Akakpo
Akosombo International, GH
Kollegio has really helped me with evaluating my essays and getting quick feedback on my essay structure! It's a much needed companion tool to the traditional college admission services, and I'm so glad that it's free because every student can benefit from it.
INFO CENTER
And more helpful info, just for you.
Yes, you read that right
Pay nothing and get the services of a $10,000 college coach
Frequently Asked
Still Unsure?
We’ve got answers. Explore our FAQs.
Or reach out at support@kollegio.ai